SunsetHost Weekly Recap: VPN Vulnerabilities, Oracle’s Quiet Data Breach, ClickFix Escalation, and More Cybersecurity Concerns
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, the threats facing individuals and organizations are more pervasive than ever. Whether it’s an unpatched system, a leaked password, or a neglected plugin, each seemingly insignificant oversight serves as an open door for cybercriminals. Supply chains, which depend on trusted code and cloud services, are no longer impervious to malicious actors, who exploit even the smallest vulnerabilities to breach systems. Malware is no longer confined to shady apps—it’s embedded in job offers, hardware, and services that companies rely on daily.
Modern hackers don’t need to leverage complex exploits; sometimes all it takes is a compromised set of credentials or a bit of social engineering to wreak havoc. This week, we take a closer look at how seemingly minor oversights have led to major breaches, as well as the ongoing threats that many organizations still underestimate. Let’s dig into the week’s major cybersecurity developments.
Threat of the Week
UNC5221 Exploits Ivanti Flaw to Deliver Malware
The notorious China-linked cyber espionage group, UNC5221, has successfully exploited a newly discovered vulnerability in Ivanti Connect Secure (CVE-2025-22457), a critical flaw with a CVSS score of 9.0. Despite Ivanti patching the issue in February 2025, UNC5221 managed to exploit unpatched systems, delivering a range of malicious tools including an in-memory dropper (TRAILBLAZE), a passive backdoor (BRUSHFIRE), and the SPAWN malware suite. This breach highlights the persistence of threat actors who actively reverse-engineer patches to target outdated systems. UNC5221 has ties to broader groups such as APT27, Silk Typhoon, and UTA0178, further underlining the scope of their activities.
Top News
EncryptHub: A Lone Wolf Exposed
In a surprising twist, the EncryptHub threat actor, who had operated largely under the radar, has been exposed due to a series of security mistakes. Unlike typical cybercriminals, EncryptHub was simultaneously involved in legitimate security research, even earning recognition from Microsoft’s Security Response Center (MSRC) for discovering vulnerabilities such as CVE-2025-24061 and CVE-2025-2407. However, their darker side came to light when it was revealed that EncryptHub had used OpenAI’s ChatGPT to assist in developing malware and to translate malicious code. In one revealing conversation, EncryptHub even sought advice from the AI chatbot on whether to embrace a “black hat” or “white hat” approach, exposing the blurred lines between ethical hacking and cybercrime.
GitHub Supply Chain Breach Traced to SpotBugs PAT Theft
The cascading supply chain attack that initially targeted Coinbase has now been linked to the theft of a personal access token (PAT) from the popular static analysis tool SpotBugs. The breach, which unfolded over multiple stages, began in November 2024 and escalated through the compromise of the reviewdog/action-setup GitHub Action, leading to the exposure of sensitive information in 218 repositories. The attack initially aimed at Coinbase-related projects but spread to other targets once attackers realized their attempts had failed. The incident highlights the dangers of compromised open-source projects and the significant risks posed by the interconnected nature of modern software development.
Contagious Interviews and the Rise of ClickFix Strategy
The Contagious Interviews campaign, associated with North Korean threat actors, has seen an alarming adoption of the ClickFix social engineering technique to deploy malware. This strategy has allowed attackers to distribute the GolangGhost backdoor, along with the BeaverTail information stealer and a new remote access trojan (RAT) loader via fake npm packages. The malicious packages, which were downloaded over 5,600 times before being removed, continue to impact organizations globally. Meanwhile, North Korean operatives have extended their focus beyond U.S. borders, targeting Europe and attempting to fraudulently secure employment within various organizations. Law enforcement’s efforts to crack down on this operation have pushed the attackers to shift tactics, increasing their efforts to extort money once exposed.
Triada Malware Found in Counterfeit Android Phones
Counterfeit Android phones, often sold at a significant discount, have been found preloaded with a modified version of the Triada malware. These fake devices are primarily distributed through unauthorized channels in Russia, and experts believe that this is part of a broader hardware supply chain compromise. The malware has been known to propagate through unofficial WhatsApp mods and third-party app marketplaces, further increasing the risk of infection.
Malware Spread Through WordPress mu-Plugins
Cybercriminals are increasingly exploiting the WordPress mu-plugins directory to surreptitiously execute malicious code on every page of a site. These mu-plugins, which run automatically on every page load and are not listed in the standard plugin directory, provide attackers with an unobtrusive way to carry out various types of attacks. These include credential theft, code injection, and even altering the HTML output of websites. The use of mu-plugins for malware distribution highlights how even well-known platforms like WordPress can be exploited if proper security measures are not implemented.
Trending CVEs
This week’s list of critical vulnerabilities serves as a stark reminder of the ongoing need for vigilant patching practices. Hackers are continuously probing for these vulnerabilities to exploit. Here are the most pressing vulnerabilities of the week:
-
CVE-2025-22457 – Ivanti Connect Secure (Critical)
-
CVE-2025-30065 – Apache Parquet
-
CVE-2024-10668 – Google Quick Share for Windows
-
CVE-2025-24362 – GitHub CodeQL Action
-
CVE-2025-1268 – Canon
-
CVE-2025-1449 – Rockwell Automation Verve Asset Manager
-
CVE-2025-2008 – WP Ultimate CSV Importer Plugin
-
CVE-2024-3660 – TensorFlow Keras
-
CVE-2025-20139 – Cisco Enterprise Chat & Email
-
CVE-2025-20212 – Cisco AnyConnect VPN Server
The time to patch is now—waiting could turn a small vulnerability into a catastrophic breach.
Around the Cyber World
Oracle’s Quiet Data Breach Acknowledged
Oracle has privately confirmed a data breach that occurred in a legacy Oracle environment. Hackers managed to compromise the system, exposing sensitive data such as usernames, passkeys, and encrypted passwords. While Oracle has downplayed the severity, claiming the system had been unused for eight years, this breach contradicts their earlier public statements denying any incidents. Investigations by the FBI and CrowdStrike are ongoing. The breach is believed to have been facilitated by an unpatched vulnerability in Oracle Fusion Middleware (CVE-2021-35587), allowing attackers to exploit a 2020 Java exploit to install a web shell and exfiltrate data.
New Triton RAT on the Loose
A new Python-based remote access trojan called Triton RAT has emerged, offering threat actors remote control of infected systems via Telegram. The malware can log keystrokes, capture screen activity, gather Wi-Fi information, and steal sensitive data such as passwords and Roblox security cookies. This RAT is publicly available on GitHub, highlighting the growing ease with which cybercriminals can access and deploy powerful malware tools
U.S. DoJ Recovers $8.2M Stolen in Romance Baiting Scam
The U.S. Department of Justice (DoJ) has announced the recovery of $8.2 million worth of USDT (Tether) stolen through a romance baiting scam, previously referred to as “pig butchering.” According to a complaint filed in late February 2025, the scam targeted a woman from Ohio who lost nearly $663,352 of her life savings after engaging with a scammer via text message in November 2023. The scam began innocuously, with the fraudster discussing personal topics like hobbies and religion before convincing the victim to create an account on Crypto.com. The victim transferred her funds, believing it was a legitimate investment opportunity. However, when she tried to withdraw her funds, the scammer insisted on additional payments, claiming they were necessary for the withdrawal. Eventually, after depleting her savings, the fraudster escalated the threats, warning the victim that harm would befall her friends and family. The DoJ’s announcement comes after authorities identified over 30 victims of the scheme, which was widely perpetrated across the U.S.
ClickFix Technique Used to Deliver QakBot Malware
A rising attack method, known as ClickFix, is being used to deploy the QakBot malware. Initially observed in late 2024, ClickFix involves manipulating victims into running a harmful command under the guise of fixing common issues, such as CAPTCHA verification challenges. This endpoint compromise tactic, now gaining popularity, is posing an increasing risk to cybersecurity systems globally.
Verizon Call Filter Flaw Exposed
A significant flaw in Verizon’s Call Filter app was recently discovered by security researcher Evan Connelly. The vulnerability, which allowed unauthorized access to call logs via an unsecured API endpoint, was found on February 22, 2025. The issue stemmed from the lack of verification of the phone number used in requests to retrieve incoming call logs, leaving customers exposed to potential attacks. Verizon has since patched the vulnerability as of March 25, 2025.
GitHub Enhances Advanced Security Features
GitHub has unveiled new enhancements to its Advanced Security platform, following the discovery of over 39 million leaked secrets in repositories last year. These updates include a free organization-wide secret scanning service and the introduction of GitHub Secret Protection and a new secret risk assessment tool, aimed at giving teams a clearer understanding of their exposure to security threats.
New Security Bypasses Found in Ubuntu Linux
Three new security bypasses have been discovered in Ubuntu Linux’s user namespace restrictions, which could be exploited by local attackers to gain elevated privileges. Discovered by Qualys, these vulnerabilities in the aa-exec, busybox, and LD_PRELOAD utilities could allow attackers to bypass security measures and execute privileged kernel vulnerabilities. Ubuntu is aware of the issues and is working to implement tighter rules in its AppArmor security framework.
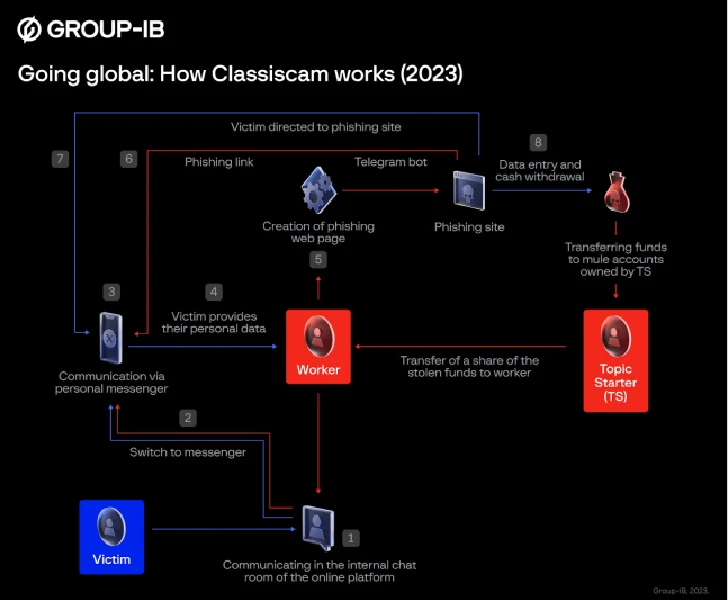
Classiscam Targets Central Asian Users
Classiscam, a scam-as-a-service operation, has been targeting financial institutions across Central Asia, particularly in Uzbekistan. Using Telegram bots, the scammers create fake websites designed to steal sensitive financial information from victims. Group-IB reports that more than ten financial institutions in Uzbekistan, including major banks and payment systems, have fallen victim to phishing attacks using these deceptive sites.
Google Partners with NVIDIA and HiddenLayer for Secure Model Signing
Google, in collaboration with NVIDIA and HiddenLayer, has introduced a Python library called model-signing, designed to enhance security in the machine learning (ML) supply chain. The library enables developers to sign and verify ML models to safeguard against emerging threats such as model poisoning and prompt injection. This initiative follows Python’s introduction of the standardized pylock.toml format, which aims to improve the security of dependency management.
Arcanum Trojan Spreads via Fortune-Telling Sites
The Arcanum Trojan is being distributed via websites masquerading as fortune-telling apps. Although initially appearing harmless, these apps deploy malicious payloads, including the Hermes stealer, Karma.Miner, and Lysander.Scytale crypto-malware. At the same time, a new credit card skimmer, RolandSkimmer, has been discovered targeting Bulgarian e-commerce sites. These two threats indicate a growing trend of malware being distributed through seemingly innocuous channels.
Rising Identity-Based Cyberattacks
Cyberattacks based on stolen credentials are increasing, with threat actors increasingly leveraging compromised user accounts to infiltrate networks. According to Cisco Talos, identity-based attacks have become a primary method of gaining access to sensitive systems. Ransomware gangs, for example, often use stolen credentials from initial access brokers (IABs) to launch attacks. Given that many users recycle passwords across different services, the risk of a widespread breach is growing, with one study showing that 41% of successful logins on Cloudflare-protected sites involved compromised credentials.
Iran-Linked OilRig Group Targets Iraqi Entities
OilRig, an Iranian hacking group, has been linked to a series of cyberattacks targeting Iraqi state entities. Using spear-phishing tactics, the group deploys a backdoor to execute commands, gather host data, and manage files via HTTP and email-based command-and-control (C2) channels. These attacks, which have been ongoing since late 2024, have been primarily aimed at Iraqi government institutions.
Security Flaws in PyTorch Lightning
Five serious vulnerabilities have been disclosed in PyTorch Lightning versions 2.4.0 and earlier, which could allow attackers to execute malicious code when loading untrusted machine learning models. These deserialization vulnerabilities arise from improper use of the torch.load() function, which could be exploited to load files containing embedded malicious code. The CERT Coordination Center (CERT/CC) has urged users to ensure that only trusted files are loaded and recommended verifying their signatures.
Russian Firm Offers $4 Million for Telegram Exploits
A Russian firm known as Operation Zero has announced it is willing to pay up to $4 million for zero-day exploits targeting Telegram. The exploit broker seeks full-chain vulnerabilities that can lead to remote code execution (RCE) on Android, iOS, and Windows platforms. The firm’s focus on Telegram is notable, given the app’s popularity in both Russia and Ukraine. Telegram has since confirmed that its platform has never been vulnerable to zero-click exploits, despite the bounty on offer.
Most Common Passwords in RDP Attacks
A recent analysis by Specops of 15 million passwords used in RDP attacks revealed the most common weak passwords, including 123456, Password1, and Welcome1. With attackers continuously searching for exposed RDP servers, these passwords are prime targets for brute-force and password spraying attacks, making it essential for organizations to employ stronger, more secure login practices.
Expert Webinar
Shadow AI in Your Apps: How to Lock It Down
As AI tools rapidly infiltrate enterprise applications, security teams are struggling to monitor and control them effectively. Join Dvir Sasson, Director of Security Research at Reco, for a webinar that uncovers hidden AI threats inside your SaaS applications and provides practical steps for detecting and mitigating rogue AI risks.
Cybersecurity Tools
GoResolver
GoResolver, an open-source tool by Volexity, is designed to help security researchers reverse Golang malware, which is often obfuscated by tools like Garble. Integrated with popular reverse engineering platforms like IDA Pro and Ghidra, GoResolver simplifies the process of recovering hidden function names and revealing package structures.
Matano
Matano is a serverless, cloud-native security data lake for AWS, offering security teams full control over their logs without vendor lock-in. It normalizes unstructured security data in real-time, integrates with over 50 sources, and allows for powerful log transformations using VRL scripting.
Tip of the Week
Detecting Early Threats by Tracking First-Time Connections
Catch cyberattacks early by focusing on first-time connections to critical systems. Detect when an unfamiliar device, IP, or location accesses your network—this is one of the best ways to identify intrusions before malware becomes widespread. Use tools like Wazuh, OSQuery, and Graylog to automate detection of such events and flag suspicious activity immediately.
This week’s recap highlights how the cybersecurity landscape continues to evolve, with cybercriminals finding new and creative ways to exploit vulnerabilities and compromise systems. From the continued evolution of malware strategies like ClickFix to the silent breaches that even large companies struggle to detect, the risks have never been more complex. The key takeaway for organizations is clear: a single oversight—whether it’s failing to patch a vulnerability or trusting an unverified software package—can lead to devastating consequences. The threat landscape is vast and ever-changing, and proactive vigilance is essential to stay one step ahead of the attackers.
The cyber threats we face today often operate in the shadows—subtle flaws, unnoticed intrusions, and invisible attacks. This week’s updates emphasize the importance of staying vigilant and continuously scanning for risks that may not immediately sound alarms. Always keep an eye on the blind spots.
